How to Hold Your Breath for 2 Minutes dives into the intriguing world of breath-holding, shedding light on its benefits, techniques, and safety measures. Discover the secrets to unlocking your lung capacity and improving your breath control in this comprehensive guide.
Explore the physiological factors, training techniques, and safety precautions involved in the art of breath-holding to enhance your understanding and performance.
Introduction: How To Hold Your Breath For 2 Minutes

Breath-holding can have several benefits, including improving lung capacity, reducing stress, and increasing mental focus. By practicing breath-holding techniques, individuals can train their bodies to use oxygen more efficiently and strengthen their respiratory muscles. Interestingly, some free divers are able to hold their breath for several minutes due to their specialized training and techniques. This practice involves slowing down the heart rate, conserving oxygen, and staying relaxed under pressure.
Overall, breath-holding can be a valuable skill to develop for both physical and mental well-being.
Breath-Holding Techniques, How to Hold Your Breath for 2 Minutes
- Diaphragmatic breathing: Focusing on breathing deeply using the diaphragm can help expand lung capacity and improve oxygen flow.
- CO2 tolerance training: Gradually increasing the time spent holding your breath can help the body adapt to higher levels of carbon dioxide.
- Meditative practices: Techniques such as mindfulness meditation can help individuals stay calm and relaxed while holding their breath for extended periods.
Improving Lung Capacity
Breath-holding exercises can strengthen the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, leading to increased lung capacity over time. By regularly practicing breath-holding, individuals can enhance their ability to take in and utilize oxygen more effectively. This improved lung function can benefit overall physical performance, respiratory health, and endurance in various activities.
Physiological Factors
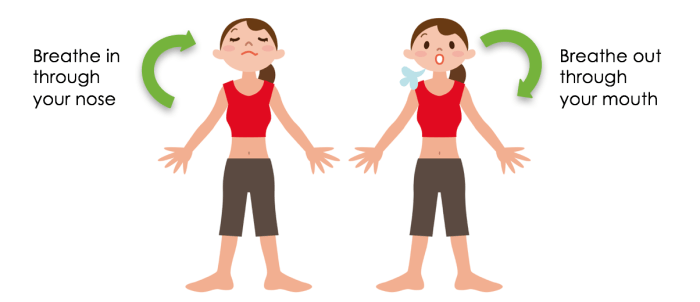
Understanding the physiological factors at play when holding your breath is crucial to achieving longer breath-holding times.
The Role of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
During breath-holding, the levels of oxygen in the body decrease, and carbon dioxide levels increase. Oxygen is essential for energy production in the body, while carbon dioxide is a waste product that needs to be eliminated.
Physiological Response
- As oxygen levels drop and carbon dioxide levels rise, the body triggers a series of responses to conserve oxygen and rid itself of excess carbon dioxide.
- Heart rate may increase to deliver oxygen to vital organs.
- Blood vessels constrict to prioritize oxygen delivery to essential tissues.
- The spleen contracts to release more oxygen-carrying red blood cells into circulation.
Brain Regulation of Breathing
The brain plays a crucial role in regulating breathing and the urge to breathe. It monitors oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood and sends signals to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to initiate breathing when needed.
Training Techniques

Breath-holding can be improved through consistent practice and proper techniques. Here are some step-by-step methods to help you safely increase your breath-holding time.
Breath-Holding Exercises
- Start by taking a deep breath and holding it for as long as you comfortably can. Gradually increase the duration as you practice regularly.
- Practice diaphragmatic breathing to strengthen your lungs and increase your lung capacity.
- Try breath-holding exercises such as CO2 tolerance training, where you exhale completely and hold your breath until you feel the urge to breathe.
Relaxation Techniques
- Focus on staying calm and relaxed during breath-holding exercises. Tension can decrease your breath-holding time.
- Practice meditation or mindfulness to help control your breath and relax your body before attempting to hold your breath.
- Use visualization techniques to imagine yourself in a peaceful environment while holding your breath, which can help distract your mind from the urge to breathe.
Safety Precautions

Breath-holding exercises can be risky if not done properly. It is essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with holding your breath for an extended period and to know when to stop to avoid any negative consequences.
Potential Risks
- Air hunger: The body’s natural response to the lack of oxygen can cause an intense urge to breathe, leading to discomfort and panic.
- Hypoxia: Prolonged lack of oxygen can result in hypoxia, which can lead to dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness.
- Hyperventilation: Over-breathing before breath-holding can reduce the body’s tolerance to high levels of carbon dioxide, increasing the risk of blackout.
Warning Signs
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Confusion or disorientation
- Blue lips or fingertips
- Irregular heartbeat
- Loss of muscle control
Guidance on Stopping
- If you experience any of the warning signs mentioned above, stop the breath-holding exercise immediately.
- Listen to your body and never push yourself beyond your limits.
- It is crucial to prioritize safety over achieving a specific breath-holding goal.
Ultimate Conclusion

In conclusion, mastering the art of holding your breath for 2 minutes requires dedication, practice, and awareness of your body’s limits. By following the tips and techniques Artikeld in this guide, you can safely improve your breath-holding skills and experience the numerous benefits it has to offer.